SpaceX’s Starlink project has captured the world’s attention as it aims to provide high-speed internet across the globe.
Starlink operates by deploying a vast network of small satellites in low Earth orbit that communicate with ground-based user terminals and ground stations to provide high-speed internet access worldwide.
The use of LEO satellites helps to reduce latency and potentially offers broadband speeds comparable to or exceeding those of ground-based internet providers.
With the increasing interest in this ambitious endeavour, several questions have surfaced regarding Starlink satellites’ nature and functionality.
In this blog post, let’s explore what is Starlink Satellite and its important functionalities.

Starlink is a satellite internet constellation being constructed by SpaceX to provide satellite Internet access.
The constellation will consist of thousands of mass-produced small satellites in low Earth orbit (LEO), working in combination with ground transceivers.
SpaceX also plans to sell some of the satellites for military, scientific, or exploratory purposes.
What does a Starlink satellite look like
From the ground, Starlink satellites can sometimes be seen as a series of small, bright white dots moving steadily across the night sky in a straight line.
This is particularly noticeable shortly after a new batch of satellites has been launched and when they are orbiting at lower altitudes before reaching their final operational positions.

Technically, the Satellite has a flat-panel design with a relatively compact and flat rectangular shape.
The main body of the satellite is outfitted with multiple high-throughput antennas on its underside for communication with the user terminals on the ground.
On the top side, there is a single solar array that extends out to power the satellite.
The satellites also feature ion thrusters powered by krypton gas, which they use for orbit raising, on-station maintenance, and deorbiting at the end of their life.
Starlink satellites are equipped with multiple high-throughput antennas and a single solar array, designed to deliver a broadband internet signal directly to consumer-end user terminals (the dishes installed at customers’ homes) and to relay signals between other Starlink satellites to improve network coverage and performance.
What is The Starlink satellite size in meters?
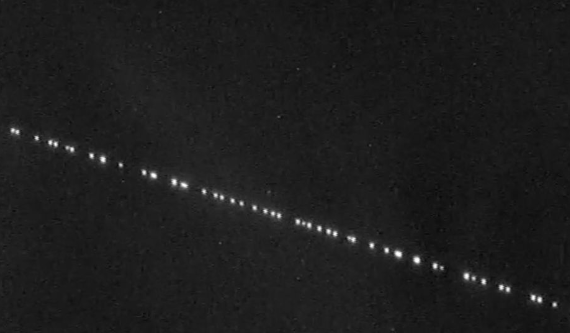
Starlink satellites are designed to be compact and efficient. Each satellite is approximately 0.3 meters (30 centimetres) wide by 2.8 meters (280 centimetres) long, with a stowed height of about 0.23 meters (23 centimetres) for launch purposes.
These dimensions contribute to the satellites’ low-profile design, which is crucial for deploying large numbers of them into orbit
are Starlink satellite geostationary?
No. Starlink satellites are not geostationary.
Geostationary satellites hover at a fixed point above the Earth’s equator, maintaining a constant position relative to the planet’s surface.
In contrast, Starlink satellites are in constant motion, orbiting the Earth in what is known as Low Earth Orbit (LEO) at altitudes of approximately 550 kilometres (340 miles)
Do Starlink satellites move or are they stationary?
Starlink satellites are indeed in motion. They traverse the sky, completing an orbit around the Earth in a much shorter period than geostationary satellites.
This movement is part of the design to create a network that provides coverage over a larger area, as each satellite moves in and out of range of different ground locations.
What type of orbit are Starlink satellites?
Starlink satellites occupy Low Earth Orbit (LEO), much closer to the Earth’s surface than geostationary orbits.
This proximity reduces the time it takes for data to travel between the user and the satellite, resulting in faster internet speeds and lower latency.
Is Starlink dish stationary?
While the Starlink dish itself is stationary in terms of its installation location, it is not static in its operation.
On the ground, users have a Starlink Kit, which includes a phased-array user terminal (often called “Dishy McFlatface” informally) to connect to the satellites, a mounting tripod, and a Wi-Fi router.
The dish is equipped with technology that allows it to automatically adjust its position to ensure optimal alignment with the Starlink satellites as they move across the sky.
How Does Starlink Satellite Move?
Starlink satellites move in orbit due to the initial velocity imparted to them by the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket that launches them into space.
Once deployed, they use this momentum to orbit the Earth in a continuous, free-fall path, circling the planet approximately every 90 minutes due to their low Earth orbit (LEO) positioning.
To adjust their orbits, maintain proper spacing, and avoid potential collisions with other objects in space, Starlink satellites are equipped with Krypton-powered ion thrusters.
These thrusters are part of the satellite’s onboard propulsion system, which can be used for a variety of manoeuvres, including:
- Orbit Raising: After deployment from the launch vehicle, satellites may need to raise their orbit to reach their designated operational altitude.
- Station Keeping: Satellites need to make small adjustments regularly to maintain their intended orbits and avoid drifting due to gravitational perturbations or atmospheric drag.
- Deorbiting: At the end of their operational life, satellites will use their thrusters to lower their orbit. This ensures they will re-enter the Earth’s atmosphere and burn up, reducing the risk of space debris.
- Collision Avoidance: If a potential collision with space debris or another satellite is detected, the thrusters can be used to adjust the satellite’s orbit to avoid the object.
These ion thrusters are highly efficient and are designed to operate for the entire lifespan of the satellite, which is several years.
The use of onboard propulsion allows SpaceX to actively manage the constellation, ensuring reliable service and compliance with space traffic management guidelines to minimize the risk of creating space debris.
FAQs
how many Starlink satellites are in orbit?
There are nearly 9,000 active satellites, with active Starlinks making up the overwhelming majority of them: 4,755. This number is constantly changing as new satellites are launched and old ones are decommissioned or re-enter the Earth’s atmosphere.
what time are the Starlink satellites tonight / How do I know when Starlink is in my area?
To find out the specific times when Starlink satellites will be visible in your area tonight, you can use various online tools and websites dedicated to tracking satellites, such as Find Starlink, James Darpinian’s satellite tracker, or In-The-Sky.org. These services allow you to enter your location to get a schedule of visible passes of Starlink satellites. The visibility can vary depending on your location, date, and local weather conditions.
Starlink satellite size and weight?
The Starlink satellites developed by SpaceX come in different versions with varying weights. As of the information available:
- The initial Starlink v1.0 satellites weigh about 260 kg (570 lb).
- The upgraded Starlink v1.5 satellites are approximately 306 kg (675 lb).
- The Starlink v2 Mini satellites are heavier, with a mass of around 800 kg (1,760 lb).
- Future Starlink v2.0 satellites are expected to be around 1,250 kg (2,760 lb).
For the dimensions, the Starlink satellites are designed to be flat and compact to fit efficiently into the Falcon 9 launch fairing. The v1.0 satellites, for example, have a flat-panel design with a single solar array wing, and each spacecraft measures about 36 feet (11 meters) end-to-end once deployed in orbit
Starlink satellite size in meters?
The dimensions of a standard Starlink satellite, such as those from the initial batches (v1.0), are roughly 2.8 meters in width and 2.3 meters in length, with a height of about 0.2 meters when stowed for launch.
How often can you see Starlink?
Starlink satellites are often visible in clusters shortly after launch, appearing multiple times a week or night. As they ascend to their operational altitude of around 550 km, they spread out, reducing their visibility. They are best seen during twilight, after sunset or before sunrise, when sunlight reflects off them against a darker sky.
What is the orbit time of a Starlink satellite?
A Starlink satellite completes an orbit around the Earth in approximately 90 to 93 minutes, depending on its specific altitude and orbital parameters. This rapid orbit allows the constellation to provide continuous coverage as the satellites move swiftly across the sky.
Can you see Starlink twice in one night?
Yes. You can see Starlink satellite multiple times in one night. Because the satellites orbit the Earth approximately every 90 to 93 minutes, and there are many satellites in the constellation, they can pass over the same location multiple times in a single night.
How many Starlink satellites are in orbit?
As of the latest available information, SpaceX has launched over 4,000 Starlink satellites into orbit. This number is constantly changing due to ongoing launches and the natural deorbiting of satellites that have reached the end of their operational life.
What happens to dead Starlink satellites?
Dead Starlink satellites use their ion thrusters to lower their orbit, increasing atmospheric drag. This process leads to a controlled deorbit, where they re-enter Earth’s atmosphere. The satellites burn up upon re-entry, preventing space debris accumulation.
How big is a Starlink?
A standard Starlink satellite, such as those from the initial batches, is roughly 2.8 meters wide, 2.3 meters long, and 0.2 meters tall when stowed for launch. These compact, flat-panel design satellites are optimized for mass deployment in SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket fairing.
How much does a Starlink satellite cost?
The exact cost of manufacturing a single Starlink satellite is not publicly disclosed by SpaceX. However, it is generally understood that SpaceX has focused on reducing the cost of each satellite through in-house manufacturing and the use of economies of scale. Some estimates suggest that each satellite could cost less than $500,000 to produce, but these figures are speculative.
How heavy is Starlink?
Starlink satellites come in various versions with different weights:
- The original v1.0 satellites weigh about 260 kg (570 lb).
- The upgraded v1.5 satellites are approximately 306 kg (675 lb).
- The Starlink V2 Mini satellites weigh around 800 kg (1,760 lb).
- Future Starlink V2.0 satellites are expected to be about 1,250 kg (2,760 lb).
Is Starlink faster than fiber?
Currently, fibre networks are generally more reliable and offer much faster speeds than Starlink’s satellite network.
What speed is Starlink?
Starlink’s internet service offers download speeds typically ranging from 50 to 200 Mbps, with some users even experiencing speeds up to 250 Mbps under ideal conditions. However, actual user experience can vary based on several factors, such as network congestion and geographical location. The service aims to provide high-speed internet access, especially in areas where traditional broadband is unreliable or unavailable.
What are the disadvantages of Starlink?
The disadvantages of Starlink include:
- Cost: The initial investment for the satellite dish and equipment, coupled with the monthly subscription fee, can be high.
- Network Congestion: During peak hours, users may experience network congestion issues and slow speeds.
- Obstructions: Service disruptions can occur due to obstructions such as trees or buildings.
- Interference with Astronomy: Starlink satellites can interfere with astronomical observations, particularly in radio astronomy.
- Less Reliable Than Cable: While improving, satellite internet is generally less reliable than cable internet.
- Self-Installation: Customers are required to install the equipment themselves, which can be a disadvantage for some users.
- Customer Service: There have been reports of poor customer service experiences by some users.
Is Starlink profitable?
As of the information available up to early 2023, Starlink, operated by SpaceX, had not yet reached profitability. While the service saw significant revenue growth, reporting $1.4 billion in revenue for 2022, it fell short of growth expectations and had not achieved a profit according to reports from that time. However, SpaceX projected that Starlink could break even and potentially become a $10 billion business in the future.
In which countries is Starlink available?
As of the latest available data, Starlink is available in over 40 countries across various continents, including North America, Europe, Australia, South America, and parts of Asia and Africa.
Why did Starlink fail?
Starlink has faced criticism for problems like network congestion and slower-than-expected speeds during peak usage, these issues are common in the early stages of deploying a new technology and are often addressed over time as the system matures and capacity is increased.
What is the Starlink satellite train schedule?
The schedule for when you can see the Starlink satellite train depends on your specific location and the time of day. To find out when you can see a train of Starlink satellites, you can use dedicated satellite trackings websites such as findstarlink.com, James Darpinian’s satellite tracking, or the Heavens-Above website.
What is special about Starlink?
- Starlink aims to provide high-speed internet access across the globe, including remote and rural areas where traditional broadband is not available.
- Unlike traditional geostationary satellite internet services, Starlink operates at low Earth orbit, which significantly reduces latency to levels comparable with ground-based broadband.
- Starlink uses phased array antennas and advanced satellite-to-satellite communication, which allows for more efficient and reliable internet service.
How many satellites will Starlink have?
The company has received approval from the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to operate nearly 12,000 satellites and has sought approval for up to 30,000 additional satellites beyond that. The exact number of satellites that will ultimately be launched can vary based on regulatory decisions, technological advancements, and business needs as the project progresses.
