We are excited to share with you our comprehensive guide on the 2G-6G journey, providing you with all the information you need to know about the evolution of mobile networks.
From the early days of 2G to the latest 6G technology, we have covered everything in detail to help you understand how the industry has transformed over the years.
2G Technology
2G, also known as second-generation technology, was introduced in the 1990s and enabled voice calls and text messages.
The technology was based on circuit-switched networks that allowed a limited amount of data to be transferred over the network.

2G technology brought a significant transformation to the mobile industry, making it possible for people to communicate while on the go.
2G Technology Components
2G (Second Generation) technology, which succeeded the first generation (1G) analog technology, is a digital technology. Here are the primary components of a 2G network:
1. Mobile Stations
This includes mobile equipment like cell phones and SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) cards that carry the user’s unique identity.
2. Base Station Subsystem (BSS)
This is composed of the Base Transceiver Station (BTS) that houses the radio transceivers and handles the radio link protocols with the Mobile Station, and the Base Station Controller (BSC) that controls multiple BTSs and manages their radio resources.
3. Network and Switching Subsystem (NSS)
Also known as the core network, it carries out call switching and mobility management. It includes components like the Mobile Switching Center (MSC), Visitor Location Register (VLR), Home Location Register (HLR), Authentication Center (AUC), and Equipment Identity Register (EIR).
4. Operation and Support System (OSS)
This is responsible for network management, controlling operations, and maintenance tasks.
5. Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN)
This is the aggregation of the world’s circuit-switched telephone networks, providing infrastructure and services for public telecommunication.
6. Databases
These include various databases like HLR, VLR, AUC, and EIR that store important information about mobile subscribers.
7. Signalling System No. 7 (SS7)
This is used to perform call setup, routing, and control in the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) and also in mobile networks.
Technical Specifications of 2G Technology
- 2G stands for second generation mobile technology.
- It uses digital signaling and circuit-switching technology.
- Maximum data transfer rate is 14.4 kbps.
- Supports voice, messaging, and basic data services.
- Uses TDMA or CDMA multiplexing techniques.
- Frequency bands range from 800 MHz to 1900 MHz.
- Provides better call quality and security compared to 1G technology.
- Enables international roaming and widespread adoption of mobile phones.
3G Technology
The third generation of mobile networks, 3G, was introduced in the early 2000s. It offered faster data transfer rates and enabled mobile internet access.

This technology allowed users to browse the internet, access social media, and download files on their mobile devices.
3G technology was a significant step forward in the development of mobile networks, as it made mobile internet access more accessible.
Technical Specifications of 3G Technology
- 3G stands for third generation mobile technology.
- It uses packet-switching technology and supports high-speed data transfer.
- Maximum data transfer rate is 2 Mbps for stationary devices and 384 kbps for moving devices.
- Supports voice, messaging, video calling, and high-speed data services.
- Uses CDMA or WCDMA multiplexing techniques.
- Frequency bands range from 850 MHz to 2100 MHz.
- Provides better network capacity, faster data transfer rates, and improved multimedia capabilities compared to 2G technology.
- Enables mobile internet access, mobile TV, and other advanced services.
4G Technology
The fourth generation of mobile networks, 4G, was introduced in the mid-2000s. This technology provided faster data transfer rates than 3G and enabled high-definition video streaming, online gaming, and other data-intensive activities on mobile devices.

4G was a game-changer for the mobile industry, as it offered faster speeds and higher bandwidth than previous generations of technology.
Technical Specifications of 4G Technology
- 4G stands for fourth generation mobile technology.
- It uses all-IP packet-switching technology and supports high-speed data transfer.
- Maximum data transfer rate is 1 Gbps for stationary devices and 100 Mbps for mobile devices.
- Supports voice, messaging, video calling, high-speed data services, and multimedia streaming.
- Uses OFDMA or SC-FDMA multiplexing techniques.
- Frequency bands range from 700 MHz to 2600 MHz.
- Provides higher network capacity, lower latency, and improved spectral efficiency compared to 3G technology.
- Enables high-quality video streaming, online gaming, and other advanced services.
5G Technology
The latest and fifth-generation technology, 5G, was introduced in the late 2010s. 5G technology offers ultra-fast data transfer rates, low latency, and massive connectivity.
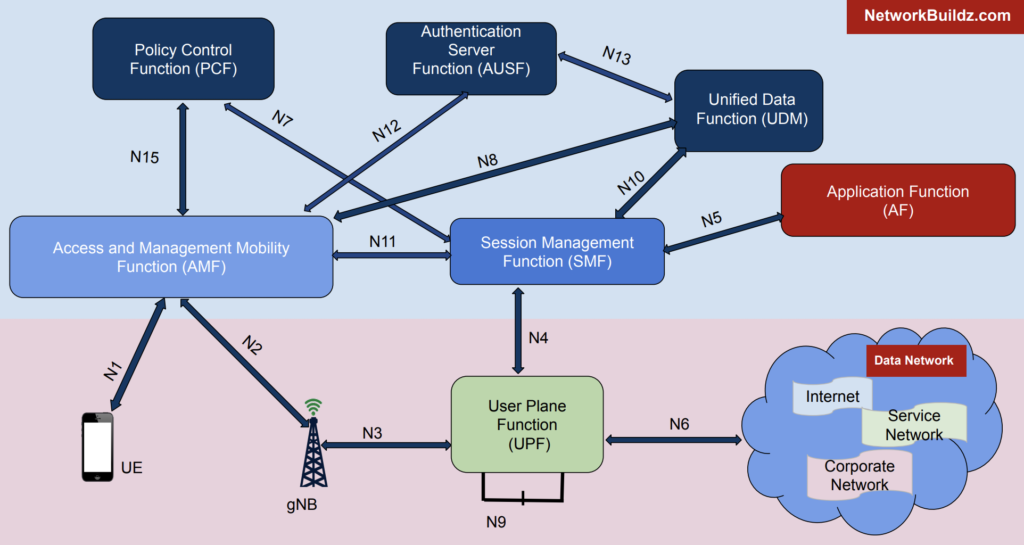
It enables real-time applications such as remote surgery, self-driving cars, and smart cities. 5G technology is a significant step forward in the evolution of mobile networks, offering unparalleled speeds and connectivity.
Technical Specifications of 5G Technology
- 5G stands for fifth generation mobile technology.
- It uses advanced wireless technologies, such as millimeter wave, sub-6 GHz, and Massive MIMO.
- Maximum data transfer rate is 20 Gbps for stationary devices and 10 Gbps for mobile devices.
- Supports voice, messaging, video calling, high-speed data services, and low-latency applications, such as remote surgery and autonomous vehicles.
- Uses advanced multiplexing techniques, such as beamforming and network slicing.
- Frequency bands range from 600 MHz to 52 GHz.
- Provides higher network capacity, faster data transfer rates, lower latency, and improved energy efficiency compared to 4G technology.
- Enables new applications, such as augmented reality, virtual reality, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
The Future of Mobile Networks (6G)
The mobile industry has come a long way since the introduction of 2G technology. With the advancements in technology, the future of mobile networks looks promising.
The introduction of 5G technology has opened up new opportunities for innovation, and we can expect to see many more advancements in the years to come.
However, some potential areas of focus for 6G technology include:
- Extremely high data rates, potentially up to 1 Tbps or higher.
- Extremely low latency, potentially less than 1 ms.
- Greater energy efficiency and sustainability.
- Advanced wireless technologies, such as terahertz frequency bands and AI-driven networks.
- New types of services and applications, such as haptic communication and immersive extended reality (XR). It’s important to note that these are only potential areas of focus for 6G and may change as the technology develops.